Arduino: Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
This is my second post detailing my Arduino Robot Car project. I will focus on using an ultrasonic distance sensor to detect obstacles and coming up with a simple algorithm to keep the car from crashing into stuff. Here is a quick video displaying the progress that can be achieved by the end of this tutorial.
It may not be the most intelligent little robot car yet, but it does OK at not running into stuff. For this post, the focus was to test out various scenarious and to get a feel of how to come up with a good solution. My next post will be an optimization of the “avoidance” algorithm.
Preparation
Unfortunately, we are going to scratch a little bit of the work you did in the last post: the switch pin. I used it in the beginning of my last project to follow along with the Arduino tutorial for motor control, and decided to leave it in the first part of my project to help me debug if something went wrong. However, now I have removed that part of the circuit and shifted some of the connections to make it more compact.
Also, you are going to have to somehow fit your Arduino, breadboard, 9V battery, and AA battery back onto your car. I am using two-sided tape so I can move things around if I need to (and I had it lying around at home). Here is a picture of what I came up with:
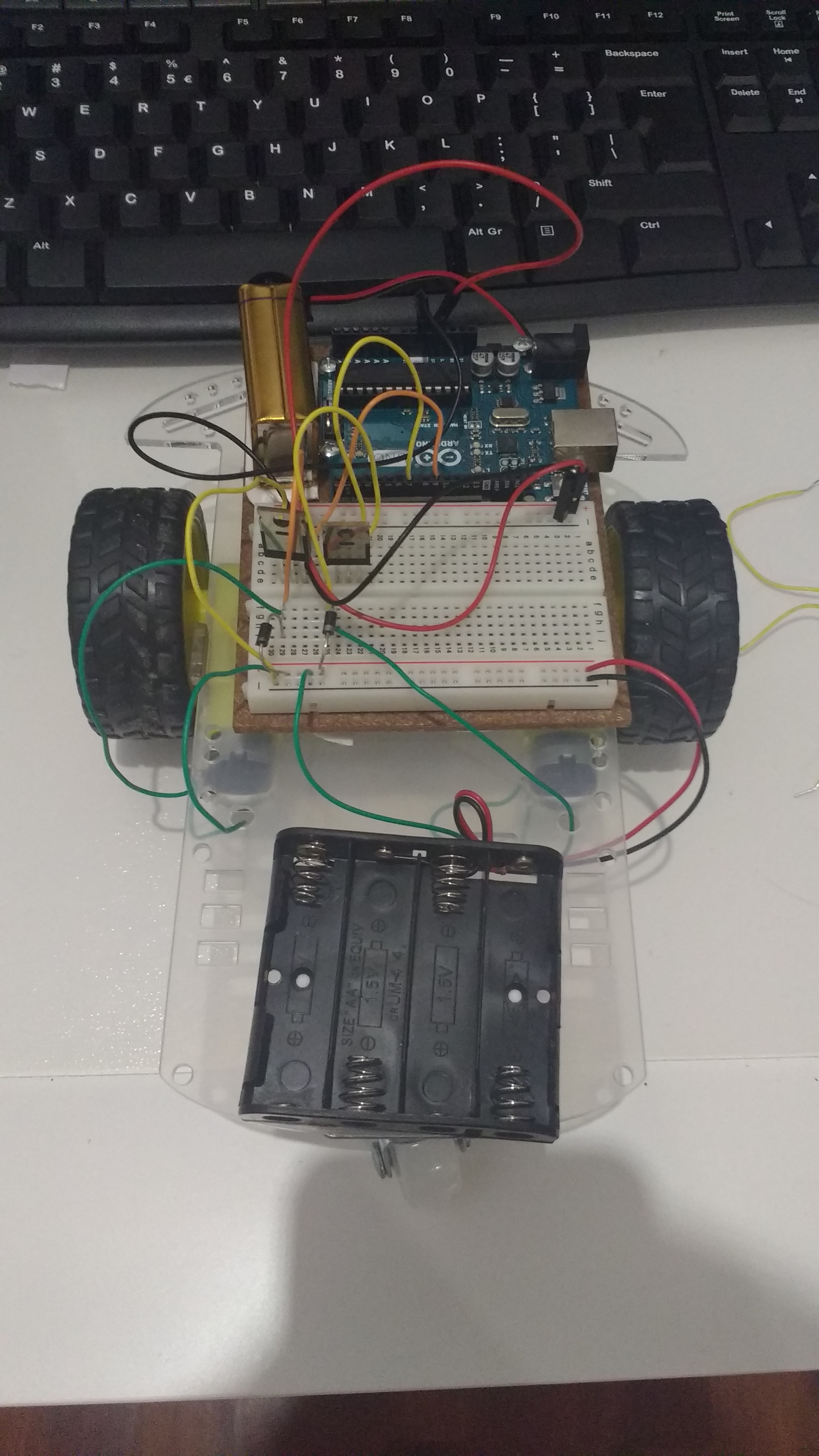
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
I am using an ultrasonic distance sensor with the New Ping Library. If you scroll down to the Connection Example, you will see the following image:
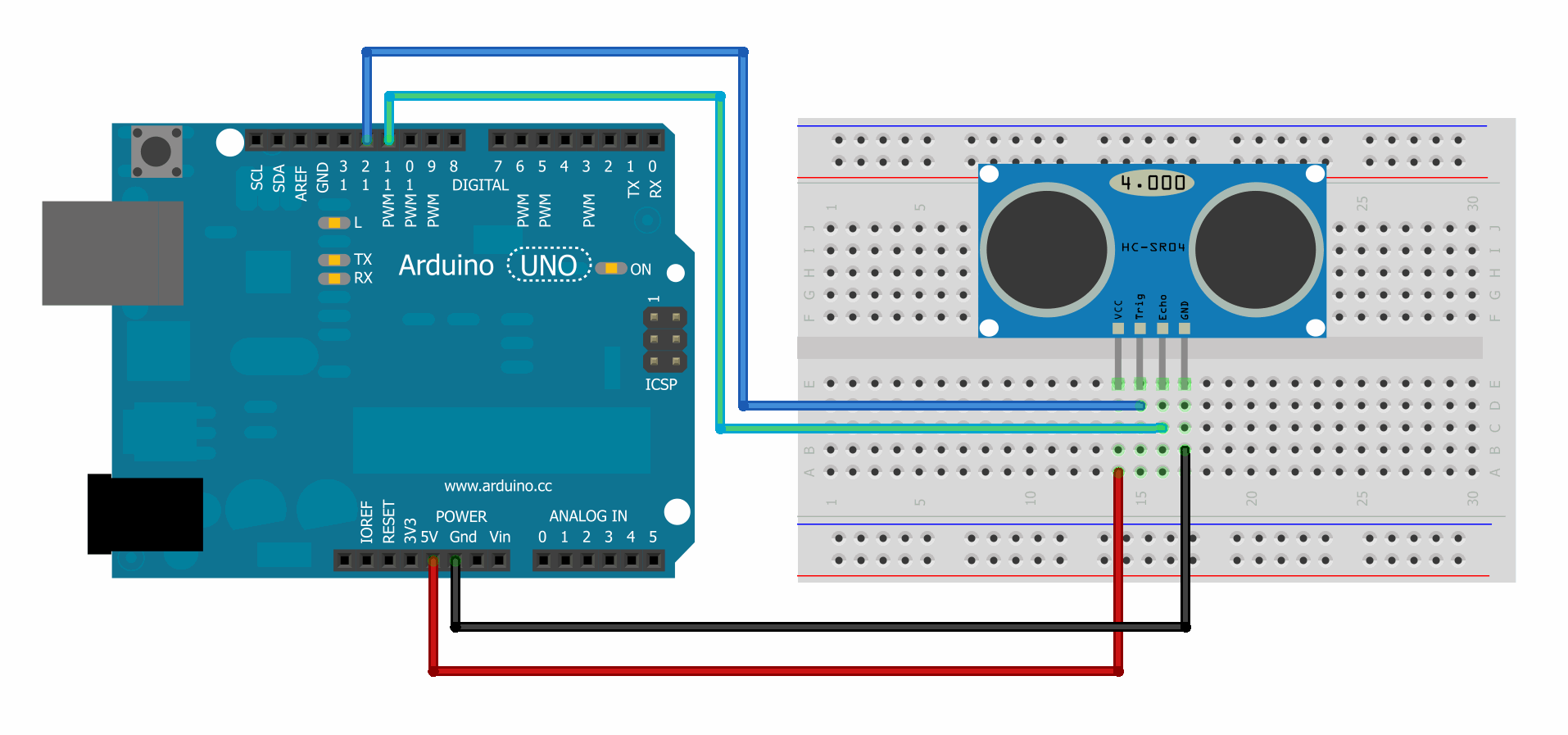
We are going to make 4 connections:
- power
- ground
- trigger: causes module to send out a Ping
- echo: receives the Ping
We are going to follow the example code given to us in the Simple NewPing Sketch example:
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example NewPing library sketch that does a ping about 20 times per second.
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <NewPing.h>
#define TRIGGER_PIN 12 // Arduino pin tied to trigger pin on the ultrasonic sensor.
#define ECHO_PIN 11 // Arduino pin tied to echo pin on the ultrasonic sensor.
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200 // Maximum distance we want to ping for (in centimeters). Maximum sensor distance is rated at 400-500cm.
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE); // NewPing setup of pins and maximum distance.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Open serial monitor at 115200 baud to see ping results.
}
void loop() {
delay(50); // Wait 50ms between pings (about 20 pings/sec). 29ms should be the shortest delay between pings.
unsigned int uS = sonar.ping(); // Send ping, get ping time in microseconds (uS).
Serial.print("Ping: ");
Serial.print(uS / US_ROUNDTRIP_CM); // Convert ping time to distance and print result (0 = outside set distance range, no ping echo)
Serial.println("cm");
}Let’s put the sensor on our robot car with the trigger connected to Digital Input 12 and the echo connected to Digitial Input 11. This corresponds to the code given to us in the Simple NewPing Sketch. Make sure that your breadboard connects to your Arduino as in the following photos:
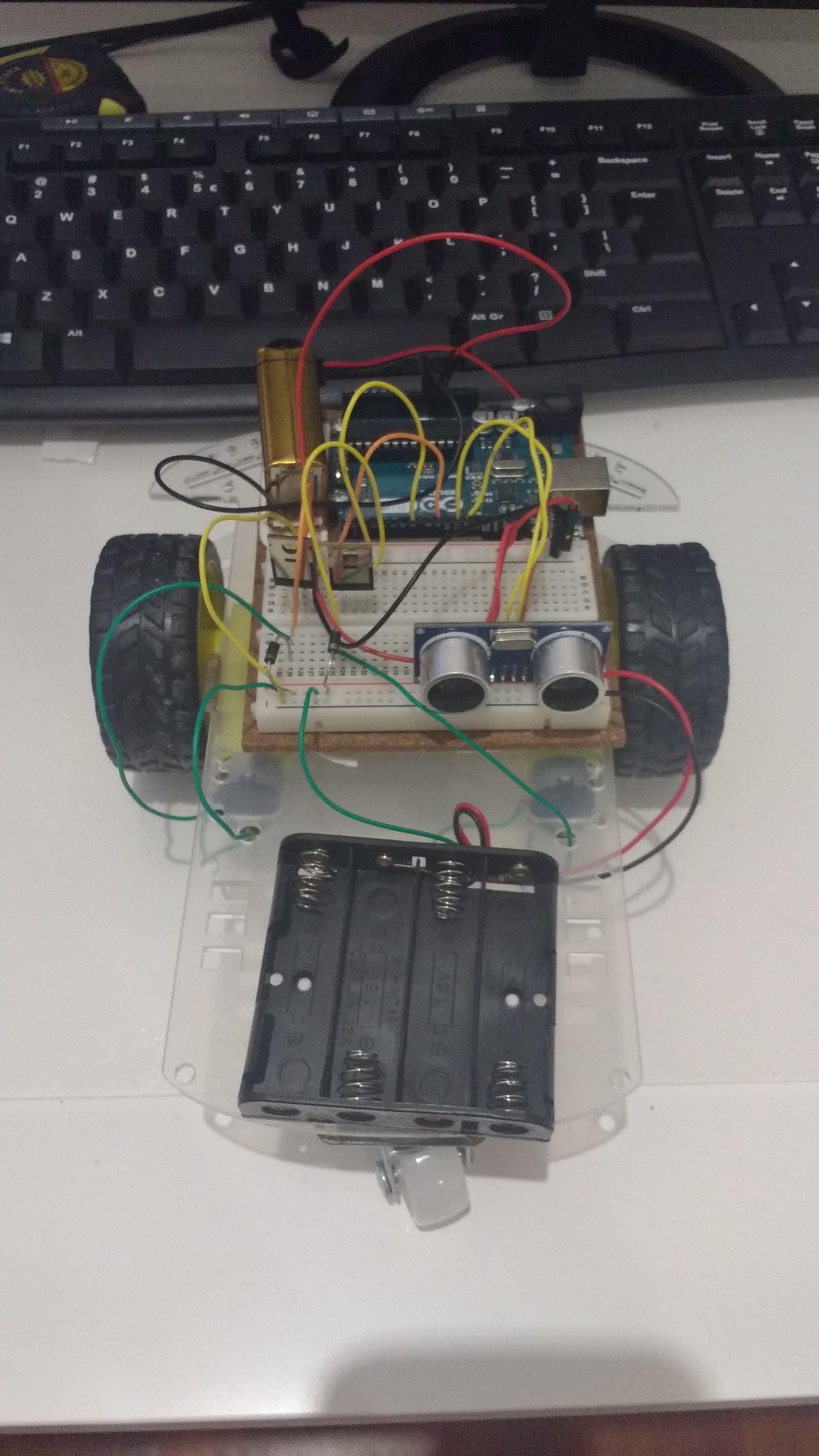
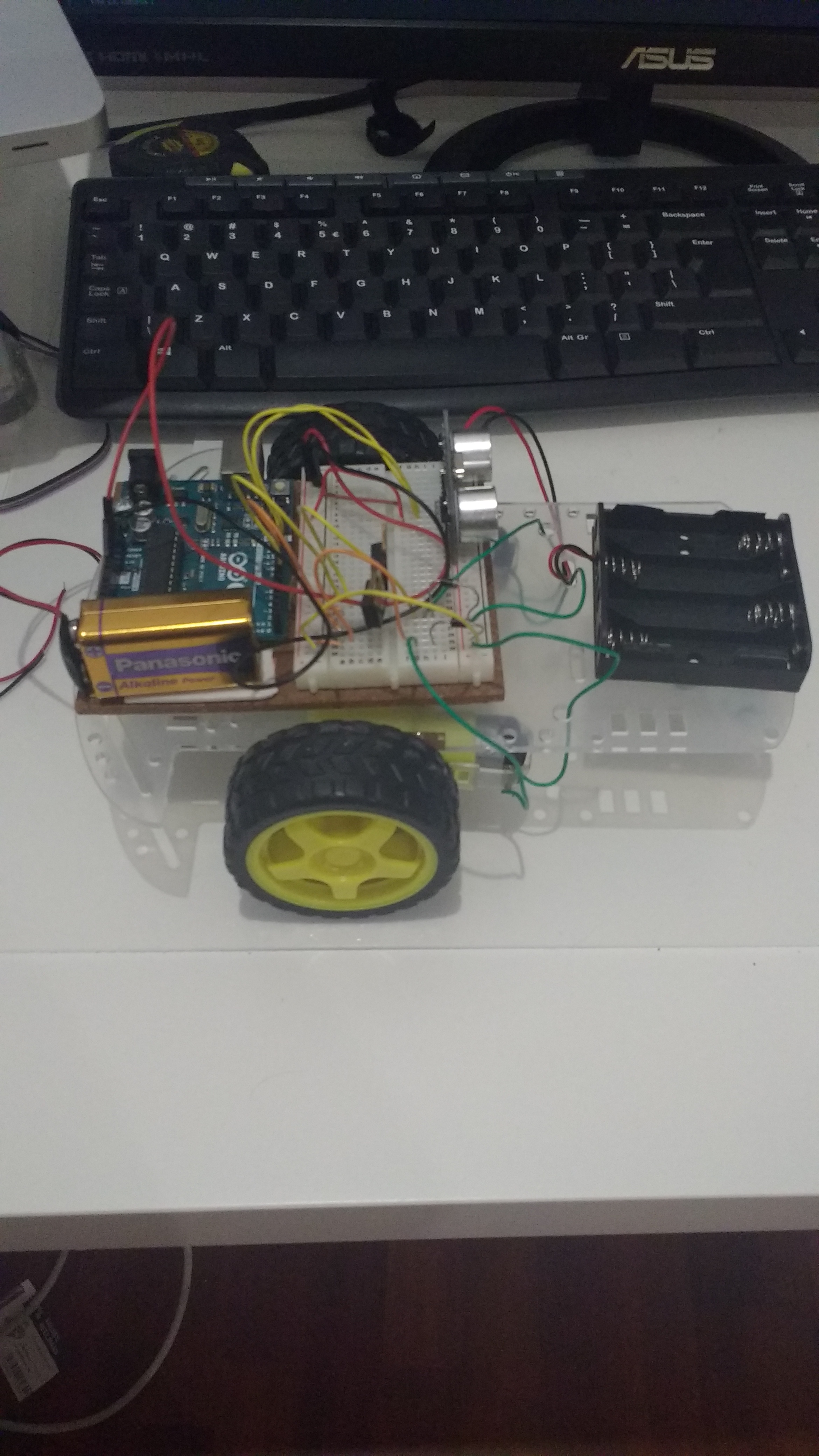
Here is my code:
#include <NewPing.h>
#define TRIGGER_PIN 12
#define ECHO_PIN 11
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE);
const int leftMotor = 9;
const int rightMotor = 7;
const int distanceToStop = 50; // approx distance my car needs to stop
void setup() {
pinMode(leftMotor, OUTPUT);
pinMode(rightMotor, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
delay(50);
unsigned int uS = sonar.ping(); // send ping and gets time in milliseconsds (uS)
unsigned int distance = uS / US_ROUNDTRIP_CM;
Serial.print("Ping: ");
Serial.print(distance); // Converßt ping time to distance and print result (0 = outside set distance range, no ping echo)
Serial.println("cm");
if (distance > distanceToStop) {
digitalWrite(leftMotor, HIGH);
digitalWrite(rightMotor, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(leftMotor, LOW);
digitalWrite(rightMotor, LOW);
delay(1000); // stop for one second
while (distance < distanceToStop) {
delay(50);
uS = sonar.ping();
distance = uS / US_ROUNDTRIP_CM;
digitalWrite(leftMotor, HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(leftMotor, LOW);
}
}Conclusion
This will give you the video that you saw in the beginning. When I try it, it will work for awhile, and then get stuck in a weird corner where the algorithm doesn’t really know what to do. It will just kinda spin around and get trapped. So, there are two things that we need to do:
- write a better algorithm
- reverse the motor direction in case we get stuck
These will be covered in the next post.